The History of Cognac: From its Origins to the Present Day
The famous French spirit, is appreciated by connoisseurs around the world for its refined taste and complex aromas. But do you really know the history of cognac, from its origins to the present day? In this article, we invite you to dive into the great historical facts of this nectar and discover how it has conquered the palates. This reading will allow you to better understand the evolution of cognac and to appreciate maybe even more this exceptional spirit.
The beginnings of cognac : The historical and geographical context
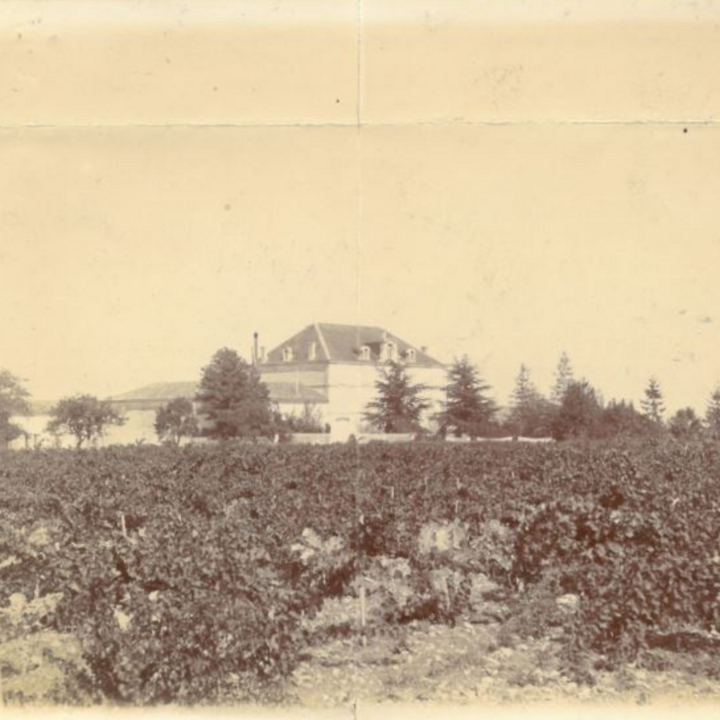
Cognac takes its name from the town of Cognac, located in the French region of Charente. The origins of this spirit go back to the 16th century, when the Dutch, great wine lovers, discovered the wines of the region. However, to facilitate the transport and the conservation of the wine, they have the idea to distill it in order to obtain a eau-de-vie known as brandwijn.
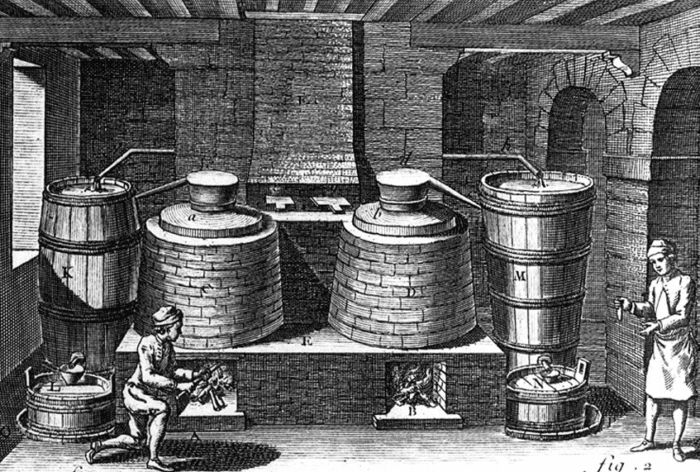
In 1610, legend has it that a certain Chevalier de la Croix-Maron had the idea of redistilling this “brandwijn” a second time, which gave birth to the technique of double distillation, which made it possible to obtain a more refined product of better quality. This is how cognac was born, a double distilled wine eau-de-vie aged in oak barrels.
The development of the cognac industry
In the 17th and 18th centuries, the cognac experienced a real boom. The growing demand, especially in England, encouraged the development of production and the establishment of several cognac houses such as Hennessy, Rémy Martin, Martell, Delamain and Hine.
Thereafter, the signature of the free trade agreement between France and England in 1860. Initiated by Napoleon III, led to an increase in cognac sales to 478,000 hectoliters in 1879, with the rise of companies such as Courvoisier, Camus, Meukow, Hardy and Jean Fillioux in 1894.
Over the years, the cognac houses have perfected their distillation, assembling and aging techniques. The cellar masters, true artisans of cognac, play a crucial role in the elaboration of this precious nectar, selecting the best eaux-de-vie and assembling them with precision to create cognacs of exceptional quality.
The regulation and protection of cognac
In order to protect and guarantee the quality of cognac, several regulations have been put in place over time.

The cognac production region was thus delimited in 1909 and counts six crus which are :
- Grande Champagne (where we are situated).
- Petite Champagne
- Borderies
- Fins bois
- Bons bois
- Bois ordinaires
Cognac is an appellation of controlled origin (AOC). It is made according to strict specifications. The BNIC (1), recognized as the ODG (2), guarantees the respect and evolution of these specifications. The specifications of the “Cognac” appellation were approved by the decree n° 2015 – 10 of January 7, 2015 then revised on October 10, 2022.
Cognac in the 21st century
Today, cognac has conserved its prestige and refinement while reinventing itself to adapt to new trends, exploring unsuspected horizons thanks to the ingenuity of the cellar masters.
With respect for secular traditions and terroirs, they succeed in creating audacious assemblies, revealing new aromas and surprising the most exigent palates, while assuring that the production practices respect the environment.
Ancestral know-how is transmitted to future generations, allowing cognac to continue to seduce a diverse and demanding audience.
As a result, it is recognized as one of the greatest achievements in the art of distillation, a cultural and gastronomic heritage that remains a timeless symbol of French excellence in the field of spirits.

Glossary :
- The “Bureau national interprofessionnel du cognac” (BNIC) is a French interprofessional organization with public service missions. It groups together all the winegrowers and merchants of the cognac production region.
- The “Organisme de Défense et de Gestion” (ODG) Cognac is an entity of the Bureau National Interprofessionnel du Cognac whose mission is to manage and follow the Cognac specifications, while ensuring the application of the control plan of the appellation.